Gastrointestinal colonisation and systemic spread of Candida albicans in mice treated with antibiotics and prednisolone - ScienceDirect
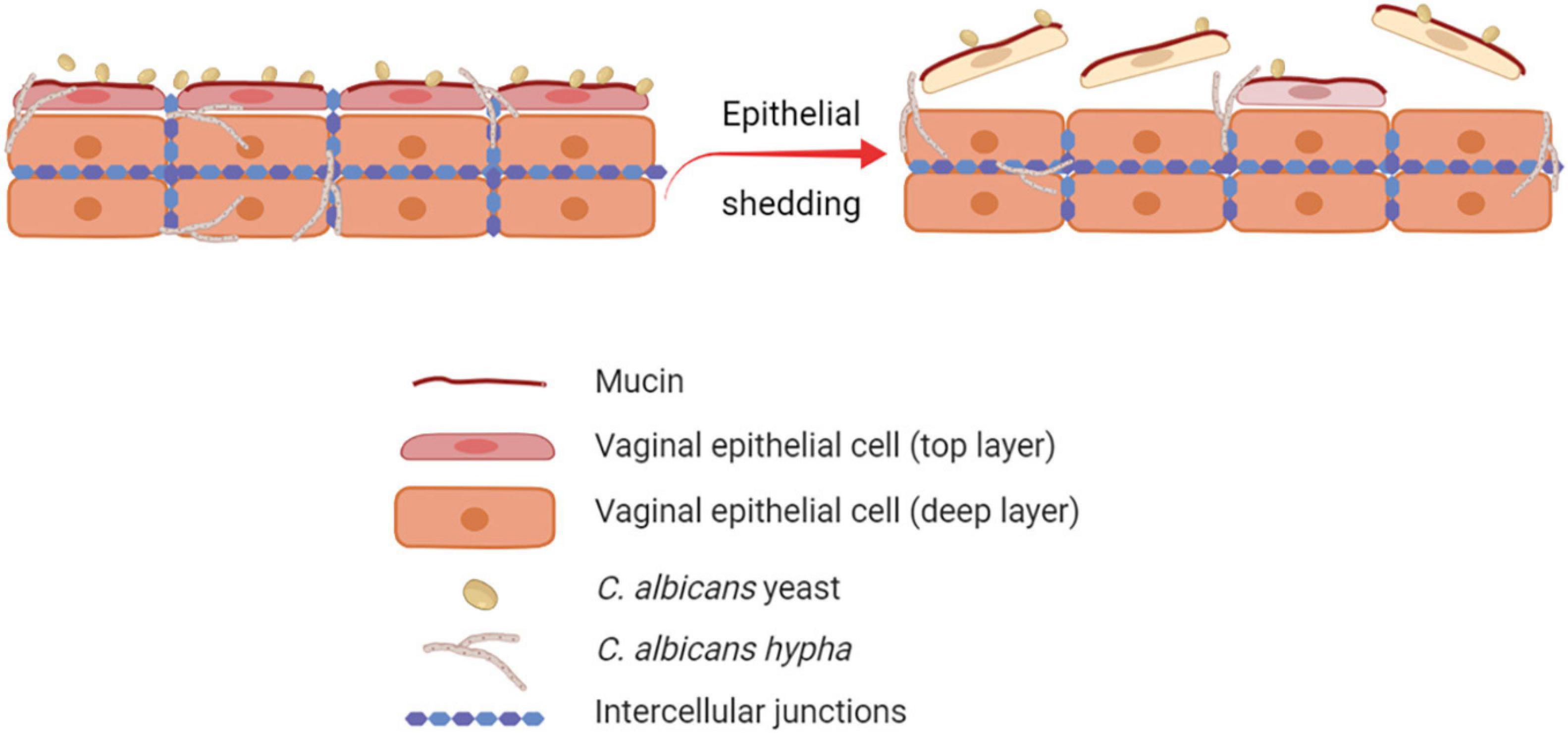
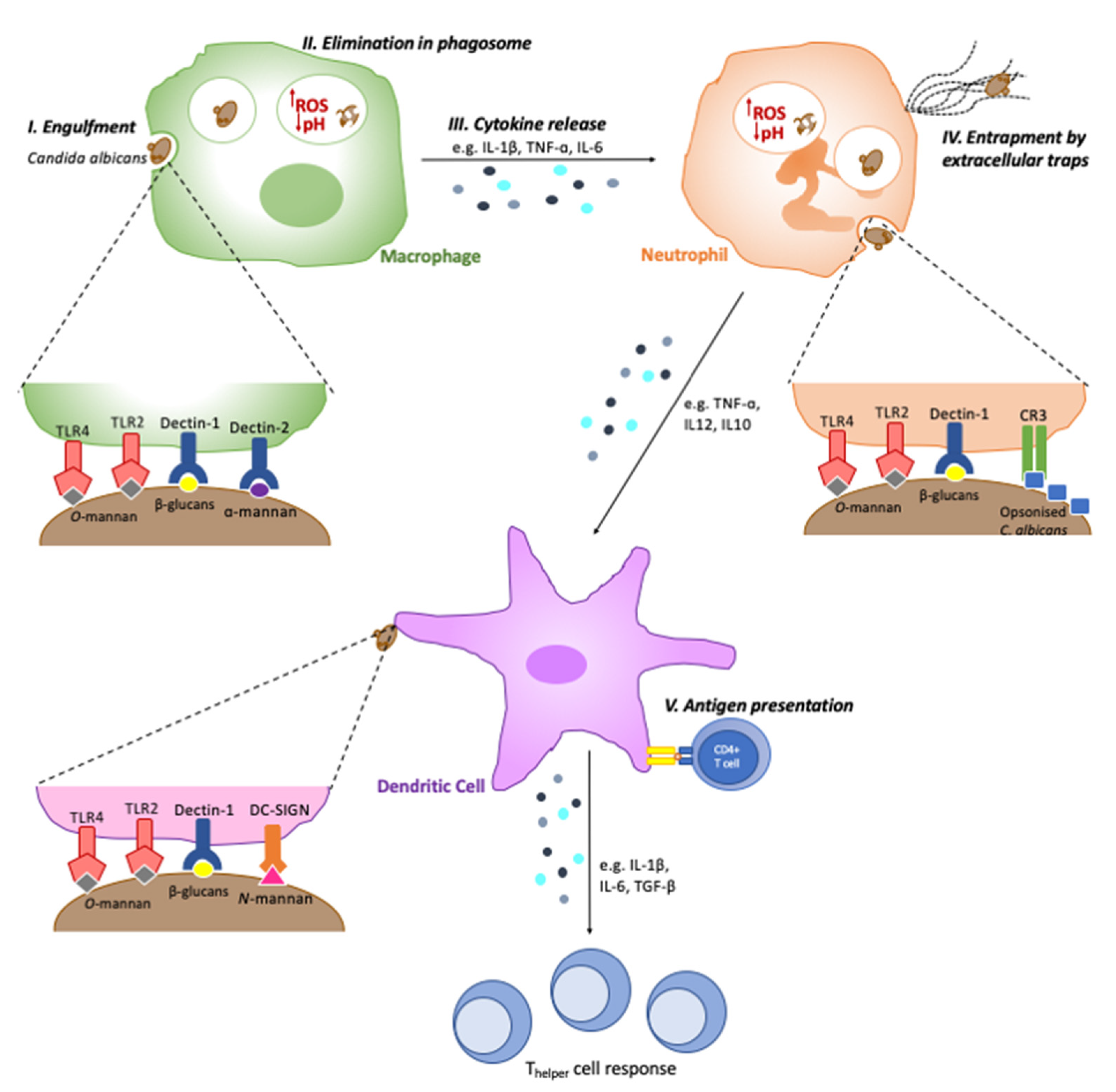
Frontiers | It Takes Two to Tango: How a Dysregulation of the Innate Immunity, Coupled With Candida Virulence, Triggers VVC Onset
Type I Interferons Promote Fatal Immunopathology by Regulating Inflammatory Monocytes and Neutrophils during Candida Infections | PLOS Pathogens

Paeoniflorin augments systemic Candida albicans infection through inhibiting Th1 and Th17 cell expression in a mouse model - ScienceDirect
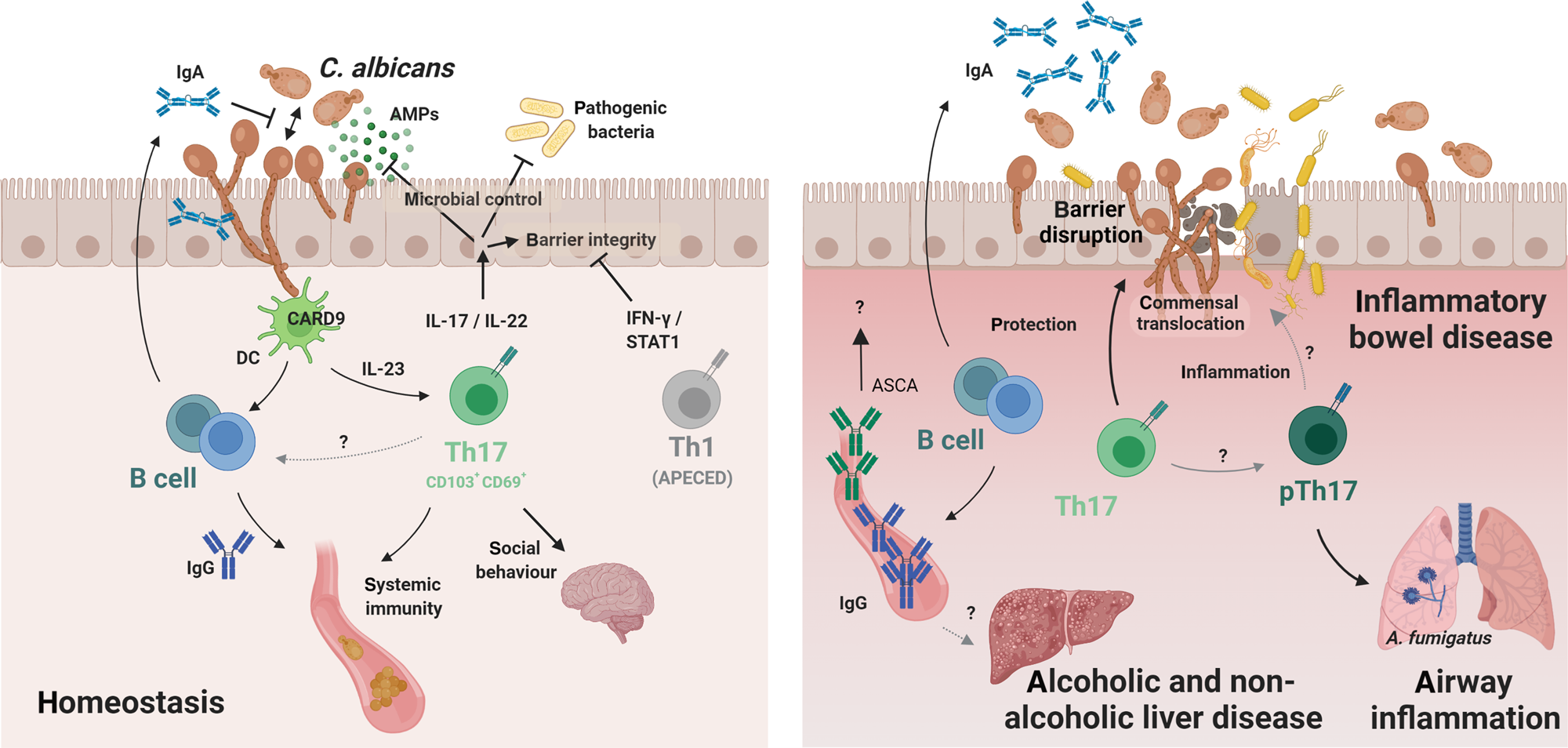
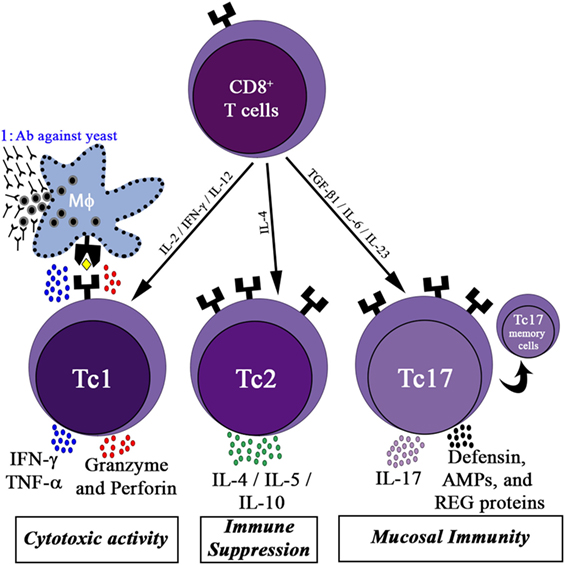
Immunosurveillance of Candida albicans commensalism by the adaptive immune system | Mucosal Immunology

EphA2 Is a Neutrophil Receptor for Candida albicans that Stimulates Antifungal Activity during Oropharyngeal Infection - ScienceDirect

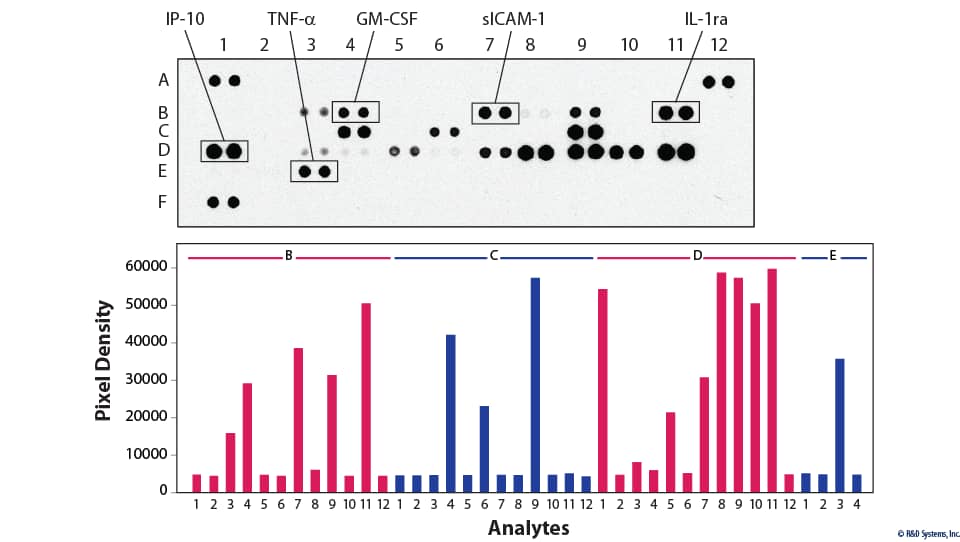
PDF) Increased susceptibility to systemic candidiasis in interleukin-6 deficient mice 1: IL6−/− mice are more susceptible to C. albicans infection
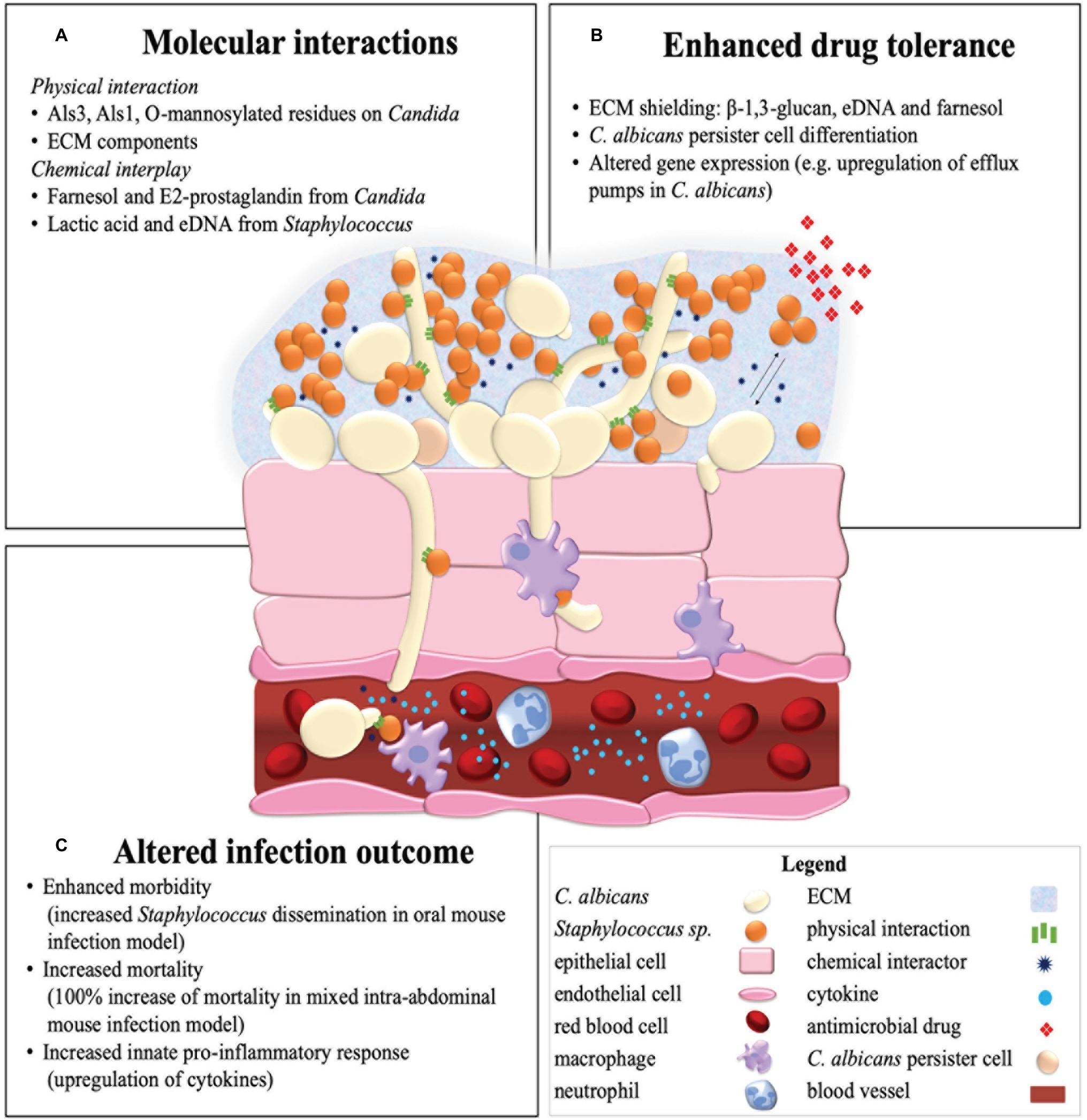
Candida albicans induces mucosal bacterial dysbiosis that promotes invasive infection | PLOS Pathogens

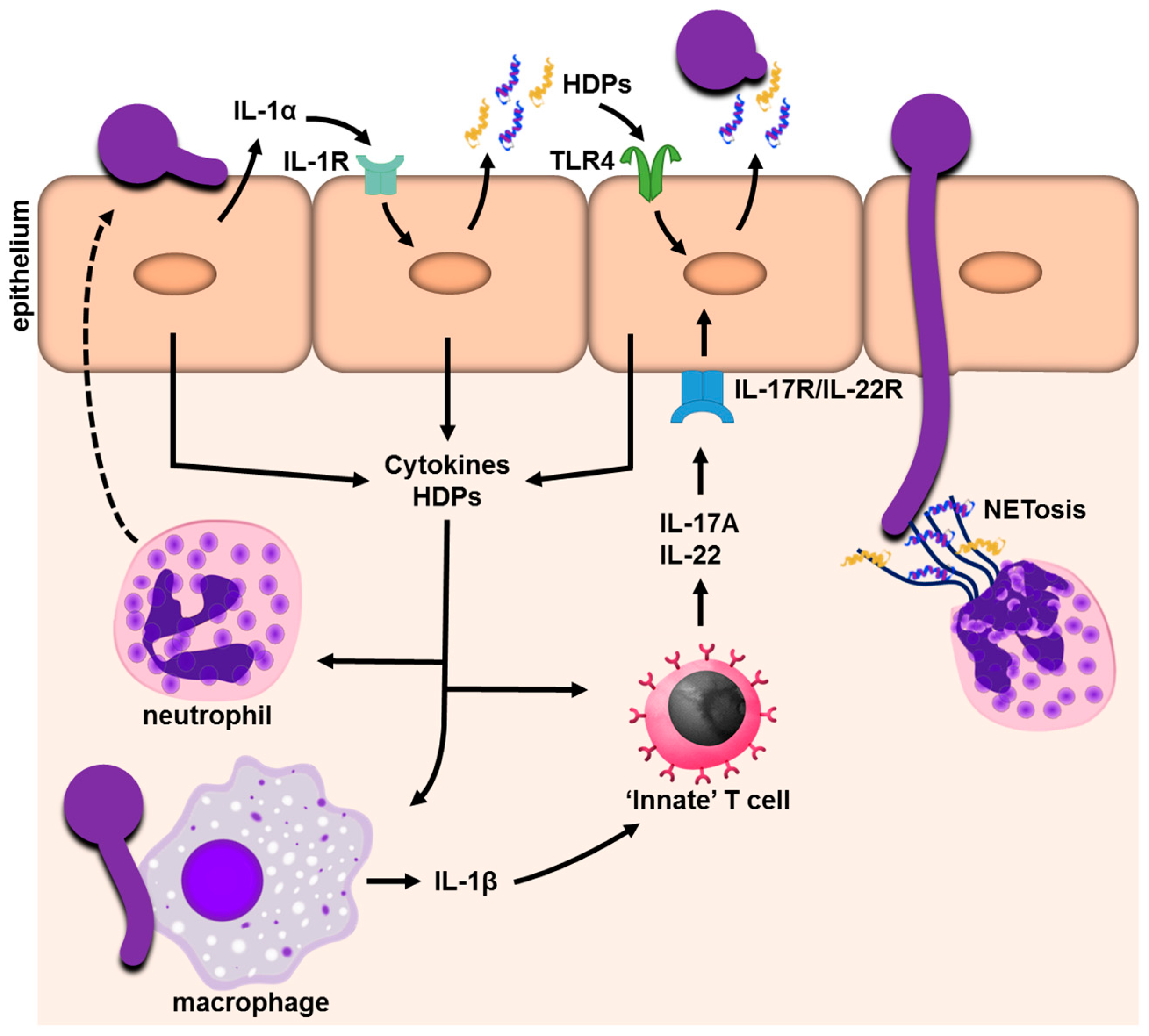
Frontiers | New Insights in Candida albicans Innate Immunity at the Mucosa: Toxins, Epithelium, Metabolism, and Beyond